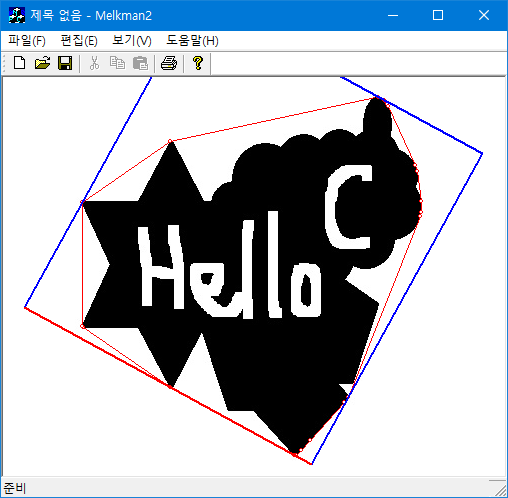
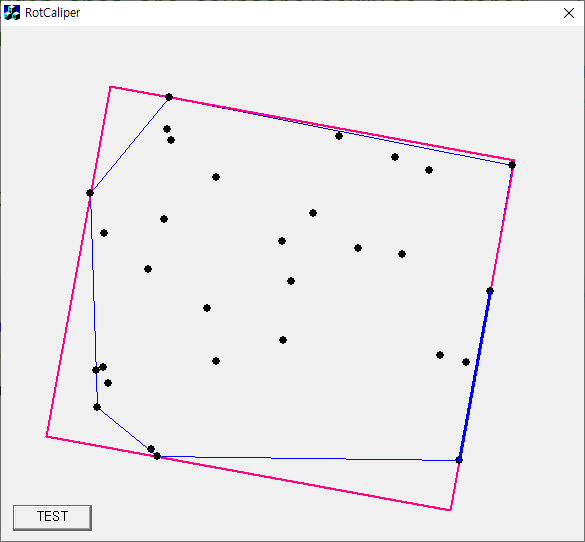
주어진 점들을 감싸는 최소 면적의 직사각형은 먼저 convex hull을 구한 후 rotating caliper을 써서 구할 수 있다. 다음 코드는 반시계방향으로 정렬된 convex hull을 이용해서 minimum volume box을 구한다. 처음 좌표축 방향으로 정렬된 bounding box을 이용해서 가장 작은 각을 형성하는 convex hull의 한 변을 찾고, 그 변으로 만들어지는 bounding box를 구한다. 반시계방향으로 bounding box가 convex hull의 변을 순차적으로 접하도록 회전시키면서 최소 면적인 경우를 찾으면 된다. 이는 convex hull을 바닥에서 굴리면서 bounding box을 찾는 경우로 생각해 보면 더 쉽다. bounding box가 convex hull의 모든 변을 다 순회하면 알고리즘이 종료되므로 time complexity는 $O(N)$이다.
void MinVolumeBox(const std::vector<CfPt>& chull, CfPt mvbox[4]) {
if (chull.size() < 3) return;
std::vector<CfPt> edges(chull.size());
std::vector<int> visited(chull.size(), 0); // initialized = 0;
enum {BB_NONE, BB_LEFT, BB_RIGHT, BB_BOTTOM, BB_TOP};
for (int i = 0; i < chull.size(); i++) {
const CfPt e = chull[(i+1) % chull.size()] - chull[i];
edges[i] = e / e.Norm();// make a unit vector;
}
// 먼저 좌표의 최소-최대 값을 구한다;
// index을 순환할 때, 항상 최대-최소가 (index+chull.size)%chull.size가 되게
double xmin = chull[0].x, xmax = xmin;
double ymin = chull[0].y, ymax = curr;
int left = 0, bot = 0, right = 0, top = 0 ;
for (int i = 1; i < chull.size(); i++) {
if (chull[i].x <= xmin) { xmin = chull[i].x; left = i;}
else if (chull[i].x >= xmax) { xmax = chull[i].x; right = i;}
if (chull[i].y <= ymin) { ymin = chull[i].y; bot = i;}
else if (chull[i].y >= ymax) { ymax = chull[i].y; top = i;}
}
if (chull[0].x <= xmin) { xmin = chull[0].x; left = 0;}
else if ( chull[0].x >= xmax) { xmax = chull[0].x; right = 0;}
if (chull[0].y <= ymin) { ymin = chull[0].y; bot = 0;}
else if (chull[0].y >= ymax) { ymax = chull[0].y; top = 0;}
/*____Initial mvbox Setting____*/
CfPt center = CfPt(xmin + xmax, ymin + ymax)/2;
CfPt ax0 = CfPt(1,0), ax1 = CfPt(0,1); // mvbox의 unit vectors;
CfPt eh = ax0, ev = ax1; // working unit vectors;
double hscale = (xmax - xmin) / 2;
double vscale = (ymax - ymin) / 2;
double minarea = hscale * vscale; // area / 4;
int done = 0;
while (!done) {
// edges[bot]는 chull[bot+1]-chull[bot];
// edges[bot],edges[right],edges[top],edges[left] 중에서
// 현재의 mvbox의 변(eh, ev,-eh,-ev)과 가장 작은 각(max_cosine)을 이루는
// edge를 찾음;
int iflag = BB_NONE;
double max_cosine = 0;
double cosine = eh * edges[bot];
if (cosine > max_cosine) { max_cosine = cosine; iflag = BB_BOTTOM;}
cosine = ev * edges[right]; ;
if (cosine > max_cosine) { max_cosine = cosine; iflag = BB_RIGHT;}
cosine = -eh * edges[top];
if (cosine > max_cosine) { max_cosine = cosine; iflag = BB_TOP;}
cosine = -ev * edges[left];
if (cosine > max_cosine) { max_cosine = cosine; iflag = BB_LEFT;}
switch (iflag) {
case BB_BOTTOM:
if (!visited[bot]) {// edges[bot]가 mvbox의 한변에 포함됨;
eh = edges[bot]; ev = eh.Rot90();
// 다음 변으로 회전;
visited[bot] = 1;
if (++bot == chull.size()) bot = 0;
} else done = 1;
break;
case BB_RIGHT:
if (!visited[right]) {// edges[right]가 mvbox의 한변에 포함됨;
ev = edges[right]; eh = -ev.Rot90();
// 다음 변으로 회전;
visited[right] = 1;
if (++right == chull.size()) right = 0;
} else done = 1;
break;
case BB_TOP:
if (!visited[top]) { // edges[top]이 mvbox의 한변에 포함됨;
eh = -edges[top]; ev = eh.Rot90();
// 다음 변으로 회전;
visited[top] = 1;
if (++top == chull.size()) top = 0;
} else done = 1;
break;
case BB_LEFT:
if (!visited[left]) {// edges[left]가 mvbox의 한변에 포함됨;
ev = -edges[left]; eh = -ev.Rot90();
// 다음 변으로 회전;
visited[left] = 1;
if (++left == chull.size()) left = 0;
} else done = 1;
break;
case BB_NONE: // polygon이 직사각형임;
done = 1;
break;
}
// check area of mvbox;
double len0 = eh * (chull[right] - chull[left]) / 2;
double len1 = ev * (chull[top] - chull[bot]) / 2;
double area = len0 * len1; //면적의 1/4 임;
if (area < minarea) {
minarea = area;
ax0 = eh; ax1 = ev;
hscale = len0; vscale = len1;
// box center: tt = left 기준 top-bot을 연결하는 vector/2;
CfPt tt = (chull[top] + chull[bot]) / 2 - chull[left];
double zz = ev * tt;
center = eh * len0 + ev * zz + chull[left];
}
}
eh = ax0 * hscale; // recover original scale;
ev = ax1 * vscale; // recover original scale;
mvbox[0] = center + eh + ev;
mvbox[1] = center - eh + ev;
mvbox[2] = center - eh - ev;
mvbox[3] = center + eh - ev;
}'Computational Geometry' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Approximate Convex Hull (0) | 2024.06.29 |
|---|---|
| Catmull-Rom Spline (2) (0) | 2024.06.21 |
| Natural Cubic Spline: revisited (0) | 2024.06.14 |
| Polygon Decimation (0) | 2024.06.08 |
| Centripetal Catmull-Rom Spline (0) | 2024.06.06 |