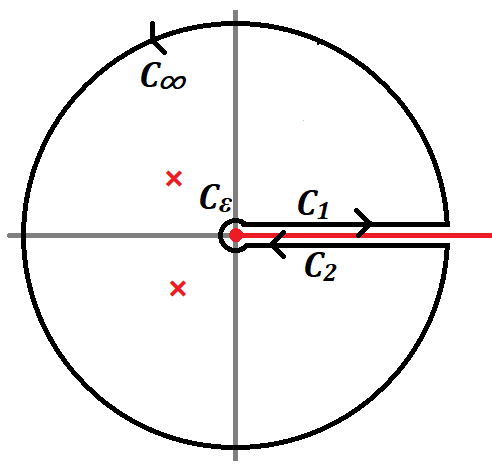
그림과 같은 복소평면상의 경로에 대해 다음 함수의 적분을 구하자.

Branch cut은
따라서
그런데
'Mathematics' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Integration along a branch cut-026 (0) | 2024.10.14 |
|---|---|
| Integration along a branch cut-025 (0) | 2024.10.12 |
| Integration along a branch cut-023 (0) | 2024.10.06 |
| Integration along a branch cut-022 (0) | 2024.10.05 |
| Integration along a branch cut-021 (0) | 2024.10.01 |