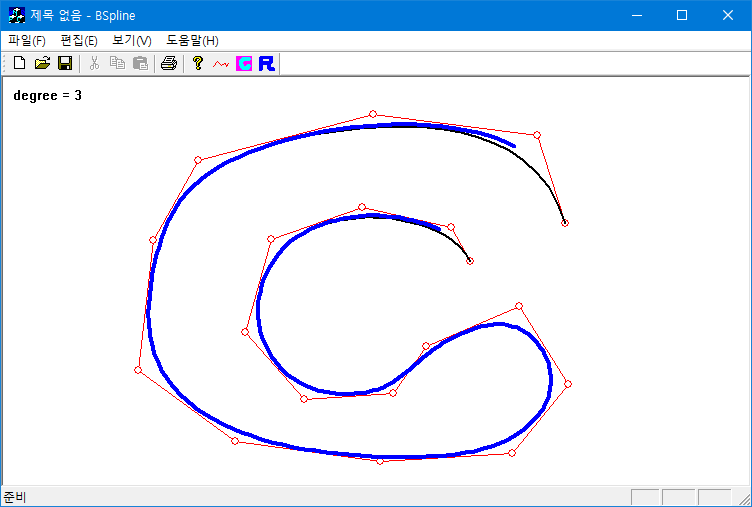
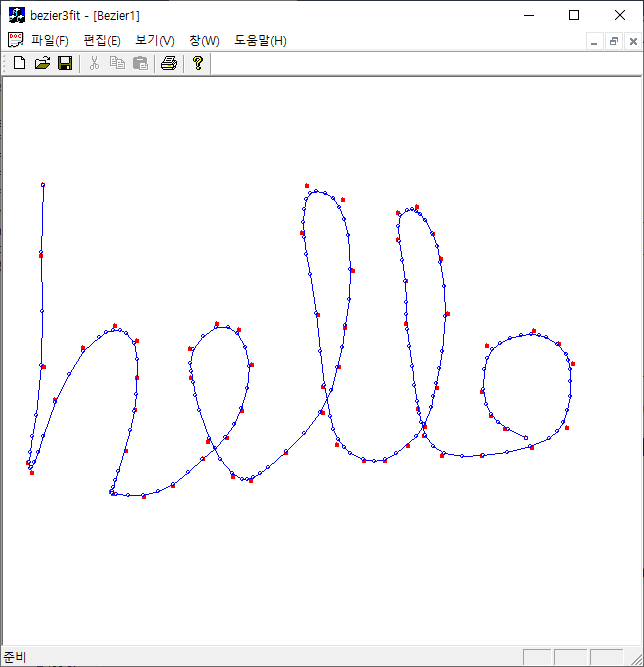
$m$개의 control point $\{\mathbf{Q}_i\}$가 주어지면 $p$차의 B-Spline curve는 basis 함수를 $N_{i, p}(t)$을 써서
$$ \mathbf{B}(t) = \sum_{i=0}^{m-1} N_{i, p}(t) \mathbf{Q}_i $$
로 표현할 수 있다. 이를 이용해서 일정한 순서로 샘플링된 평면상의 $N$개의 입력점 $\{ \mathbf{P}_i \}$을 찾아보자. B-spline 곡선을 이용하면 이 문제는 control 점을 찾는 문제가 된다. 곡선이 입력점을 잘 표현하기 위해서는 곡선과 입력점과의 차이를 최소로 하는 control 점을 찾아야 한다:
$$ \mathbf{ Q}^* = \text{argmin}(L), \quad\quad L:= \sum_{k = 0}^{N-1} | \mathbf{B}(t_k) - \mathbf{P}_k|^2 $$
여기서 $\{ t_k| k=0,1,...,N-1\}$는 입력점이 얻어지는 sample time으로 $0= t_0\le t_1\le...\le t_{N-1}= 1$로 rescale 할 수 있다.
행렬을 이용해서 식을 좀 더 간결하게 표현할 수 있다.
$$L = \sum_{k = 0}^{N-1} | \mathbf{B}(t_k) - \mathbf{P}_k|^2 = \sum_{k = 0}^{N-1} \left| \sum_{i=0}^{m-1} N_{i, p}(t_k) \mathbf{Q}_i - \mathbf{P}_k \right|^2 = \sum_{k = 0}^{N-1} \left| \sum_{i=0}^{m-1} A_{ki} \mathbf{Q}_i - \mathbf{P}_k \right|^2, \\ \quad A_{ki} = N_{i, p}(t_k) $$
로 쓸 수 있으므로, $\hat {Q}= (\mathbf{Q}_0, \mathbf{Q}_1,..., \mathbf{Q}_{m-1})^t$, $\hat {P} = (\mathbf{P}_0, \mathbf{P}_1,..., \mathbf{P}_{N-1})^t$인 벡터, 그리고 $ \hat {A} = (A_{ki})$인 행렬로 보면
$$ L= \left| \hat{A} \cdot \hat {Q} - \hat {P} \right|^2 = (\hat{Q}^t \cdot \hat {A}^t -\hat{P}^t ) \cdot (\hat{A}\cdot \hat{Q} - \hat{P}).$$
위 식의 값을 최소로 하는 최소자승해는 $\hat {Q}^t$에 대한 미분 값이 0인 벡터를 찾으면 된다; $$ \frac {\partial L}{\partial \hat {Q}^t } = \hat {A}^t \cdot \hat {A} \cdot \hat {Q} - \hat {A}^{t} \cdot \hat {P} = 0.$$ 이 행렬 방정식의 해는
$$ \hat {Q}^* = ( \hat {A} ^t \cdot \hat {A})^{-1} \cdot ( \hat {A}^t \cdot \hat {P})$$ 로 표현된다. $\hat {A} ^t \cdot \hat {A}$가 (banded) real symmetric ($m\times m$) 행렬이므로 Cholesky decomposion을 사용하면 쉽게 해를 구할 수 있다. $\hat{A}$가 banded matrix 형태를 가지는 이유는 basis가 local support에서만 0이 아닌 값을 취하기 때문이다.
open b-spline(cubic)

int BSplineFit_LS(std::vector<CPoint>& data,
int degree, // cubic(3);
int nc, // num of control points;
std::vector<double>& X,
std::vector<double>& Y) // estimated control points;
{
// open b-spline;
std::vector<double> knot((nc - 1) + degree + 2);
for (int i = 0; i <= nc + degree; i++) knot[i] = i;
std::vector<double> t(data.size()); // parameter;
double scale = (knot[nc] - knot[degree]) / (data.size()-1);
for (int i = data.size(); i-->0;)
t[i] = knot[degree] + scale * i;
std::vector<double> A(ndata * nc);
for (int i = data.size(); i-->0;)
for (int j = 0; j < nc; j++)
A[i * nc + j] = Basis(j, degree, &knot[0], t[i]); //A(i,j)=N_j(t_i)
// S = A^t * A; real-symmetric matrix;
std::vector<double> Sx(nc * nc);
std::vector<double> Sy(nc * nc);
for (int i = 0; i < nc; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < nc; j++) {
double s = 0;
for (int k = data.size(); k-->0;)
s += A[k * nc + i] * A[k * nc + j];
Sx[i * nc + j] = s;
}
}
//copy;
for (int i = nc*nc; i-->0;) Sy[i] = Sx[i];
// X = A^t * P.x; Y = A^t * P.y
for (int i = 0; i < nc; i++) {
double sx = 0, sy = 0;
for (int k = data.size(); k-->0;) {
sx += A[k * nc + i] * data[k].x;
sy += A[k * nc + i] * data[k].y;
};
X[i] = sx; Y[i] = sy;
};
// solve real symmetric linear system; S * x = X, S * y = Y;
// solvps(S, X) destories the inputs;
// ccmath-2.2.1 version;
int res1 = solvps(&Sx[0], &X[0], nc);
int res2 = solvps(&Sy[0], &Y[0], nc);
return res1 == 0 && res2 == 0;
};**네이버 블로그 이전;
'Computational Geometry' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Approximate Distance Between Ellipse and Point (0) | 2024.03.08 |
|---|---|
| Distance from a Point to an Ellipse (0) | 2024.03.06 |
| Closest Pair of Points (0) | 2021.04.27 |
| DDA Algorithm (0) | 2021.04.25 |
| B-Spline (0) | 2021.04.25 |