영상의 히스토그램($h[z]$)이 bimodal로 주어지는 경우 적절한 threshold 값을 선택해서 전경과 배경을 분리할 수 있다. 전경을 대표하는 픽셀 값을 $z_f$, 배경을 대표하는 픽셀 값을 $z_b$라면 이진화 후 정규화된 히스토그램은
$$ \tilde{h}[z] =p_b \delta_{z, z_{b}} + p_f \delta_{z, z_{f}}$$
로 표현된다. $p_b$은 배경에 해당하는 픽셀 비율이고, $p_f$은 전경에 해당하는 픽셀 비율이다.

threshold 값을 어떻게 선택하면 이진화된 영상의 히스토그램이 원 영상의 히스토그램의 특성을 최대한 담게 할 수 있을까? 이에 대한 기준으로 두 히스토그램의 $n$차 moment가 같은 값을 갖도록 하자. 주어진 미지수가 $p_b$, $p_f$, $z_b$, $z_f$이 있으므로 최소한 4개의 moment가 같도록 만들어야 한다. 가장 낮은 찾수의 moment로부터 시작해서 3차까지 4개의 moments가 같다는 조건에서 아래의 식들을 얻을 수 있다.
$$ \text{0-차 moment: } m_0 \equiv \sum_{z=0}^{255} h[z] = p_b + p_f = 1$$
$$ \text{1-차 moment: } m_1 \equiv \sum_{z=0}^{255}z h[z] = p_b z_b + p_f z_f$$
$$ \text{2-차 moment: } m_2 \equiv \sum_{z=0}^{255}z^2 h[z] = p_b z_b^2 + p_f z_f^2$$
$$ \text{3-차 moment: } m_3 \equiv \sum_{z=0}^{255}z^3 h[z] = p_b z_b^3+ p_f z_f^3$$
원 영상의 moment $m_0$, $m_1$, $m_2$, $m_3$을 계산해서 풀면
\begin{gather} c_0 = \frac{m_3 m_1 - m_2^2 }{ m_0 m_2 - m_1^2 } ,\quad c_1 = \frac{m_1 m_2 - m_0 m_3}{ m_0 m_2 - m_1^2 } \\ z_b = \frac{1}{2} \left(-c_1 - \sqrt{ c_1^2 - 4 c_0} \right) \\ z_f = \frac{1}{2}\left( -c_1 + \sqrt{ c_1^2 -4 c_0} \right) \\ p_b = \frac{z_f - m_1}{z_f - z_b} \\ p_f = 1 - p_b\end{gather}
따라서 threshold 값
$$ \sum_{z=0}^{T-1} h[z] = p_b $$
을 만족하는 $T$을 선택하면 된다.
Ref: W. Tsai, "Moment-preserving thresholding: a new approach," Computer Vision, Graphics, and Image Processing, vol. 29, pp. 377-393, 1985.
int MomentsPreseving_threshold(int histogram[256]) {
int tot = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++)
tot += histogram[i];
//normalised histogram
double hist[256];
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++)
hist[i] = double(histogram[i]) / tot;
/* moments calculation: zero moment is 1 by defintion*/
double m0 = 1, m1 = 0, m2 = 0, m3 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++ ) {
double h = hist[i];
m1 += i * h;
m2 += i * i * h;
m3 += i * i * i * h;
}
double det = m0 * m2 - m1 * m1;
double c0 = (m1 * m3 - m2 * m2) / det;
double c1 = (m2 * m1 - m3 * m0) / det;
double zb = 0.5 * (-c1 - sqrt (c1 * c1 - 4.0 * c0));
double zf = 0.5 * (-c1 + sqrt (c1 * c1 - 4.0 * c0));
double pb = (zf - m1) / (zf - zb);
double s = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++) {
s += hist[i];
if (s > pb)
return i; // threshold
}
return 0;
}'Image Recognition > Fundamental' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Canny Edge: Non-maximal suppression (0) | 2023.01.11 |
|---|---|
| Statistical Region Merging (0) | 2022.06.11 |
| Minimum Cross Entropy Thresholding (0) | 2022.05.29 |
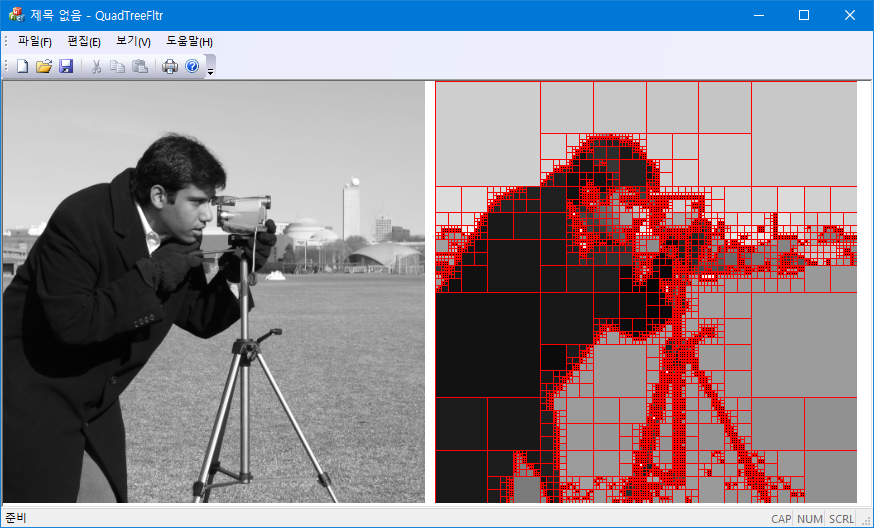
| Quadtree Segmentation (0) | 2022.05.21 |
| Harris Corner Detector (0) | 2022.04.07 |