일정한 간격 $h$마다 샘플링된 데이터 $\{ (x_k, f_k) \}$를 이용해서 이들 데이터를 표현하는 spline를 구해보자. spline은 주어진 샘플링 데이터을 통과할 필요는 없으므로 일반적으로 interpolation 함수는 아니다. 이 spline은 샘플링 데이터와 kernel이라고 불리는 함수의 convolution 형태로 표현할 수 있다.
$$ g(x) = \sum_k f_k K \left( \frac{x-x_k}{h}\right)$$
이미지의 resampling 과정에서 spline를 이용하는데 이때 사용 가능한 kernel의 형태와 그 효과를 간단히 알아보자.
3차 spline kernel은 중심을 기준으로 반지름이 2인 영역 $(-2,1),(-1,0), (0,1), (1,2)$에서만 0이 아닌 piecewise 삼차함수다. 그리고 이 함수는 우함수의 특성을 갖는다. 따라서 가능한 형태는
$$ K(s) = \left\{ \begin{matrix} A_1|s|^3 + B_1 |s|^2 +C_1 |s| + D_1 & |s| <1 \\ A_2 |s|^3 + B_2 |s|^2 + C_2 |s| + D_2 & 1 \le |s|<2 \\ 0 & \text{otherwise} \end{matrix} \right. $$처럼 쓸 수 있다. 계수를 완전히 결정하기 위해서는 8개의 조건이 필요한다. 우선 우함수이므로 원점에서 미분값이 제대로 정의되려면 $$C_1=0$$도 만족해야 한다, 그리고 각 node에서 연속성을 요구하면
\begin{align} s=1^\pm:~~~& A_1+B_1 +D_1 = A_2 +B_2+C_2 +D_2 \\ s=2^\pm:~~~& 8A_2 +4B_2 +2C_2 +D_2 =0 \end{align} 임을 알 수 있다. 또한 각 node에서 부드럽게 연결되기 위해서 1차 도함수가 연속적임을 요구하면
\begin{align} s = 1^\pm:~~~& 3A_1 + 2B_1 = 3A_2 + 2B_2+C_2 \end{align}
그리고 샘플링된 데이터가 모두 같은 경우 보간함수도 상수함수가 되는 것이 타당하므로
$$ g(x) = \sum_k K \left( \frac{x-x_k}{h}\right) = 1~~~\text{if} ~~\forall f_j = 1$$
을 만족시켜야 한다. $x_j <x<x_{j+1}$일 때 $x = x_j + sh, ~(0< s<1)$로 쓸 수 있고, kernel이 반지름이 2인 support를 가지므로
$$ g(x) = K(s+1) + K(s) + K(s-1) + K(s-2)=1$$
임을 알 수 있다. 위에서 주어진 $K(s)$을 대입해서 정리하면 다음과 같은 항등식을 얻는다.
$$ -1 + A_1 + 9 A_2 + B_1 + 5 B_2 + 3 C_2 + 2 D_1 +2 D_2 \\ +(-3 A_1 - 9 A_2 - 2 B_1 - 2 B_2) s + (3 A_1 + 9 A_2 + 2 B_1 + 2 B_2) s^2 =0$$
이 항등식의 계수가 0이 되어야 한다는 사실에서 2 개의 추가 조건을 얻으므로 총 8개 계수 중 2개가 미결정 free parameter로 남는다. 보통 이 두 계수는 $D_1=1-B/3$, $D_2=4C + 4B/3$처럼 매개화한다. 이 경우 kernel 함수는
$$ K(s) = \frac{1}{6} \left\{ \begin{matrix} (12-9B-6C)|s|^3 +(-18+12B+6C) |s|^2 + (6-2B) & |s|< 1\\ (-B-6C)|s|^3 +(6B+30C)|s|^2 + (-12B-48C) |s| + (8B+24C) & 1\le |s|<2\\0 & \text{otherwise} \end{matrix} \right.$$
따라서 cubic spline kernel은 두 개의 파라미터 (B,C)에 의해서 정해진다. 또한 kernel 함수의 적분은 $B,C$에 상관없이 항상 1이어서 총 가중치의 합이 1임이 자동으로 보증된다.
$$\int_{-\infty}^\infty K(s)ds =1$$
이 중에는 이미지의 resampling에서 많이 사용되는 커널도 있는데, 잘 알려진 경우를 보면
$$ \begin{matrix} (B,C)=(0,1) & \text{Cardinal spline} \\ (B,C)=(0,1/2) & \text{Catmull-Rom spline } \\ (B,C)=(0,3/4) & \text{used in photoshop} \\ (B,C)=(1/3,1/3) & \text{ Mitchell-Netravali spline} \\ (B,C)=(1,0) & \text{B-spline}\end{matrix}$$
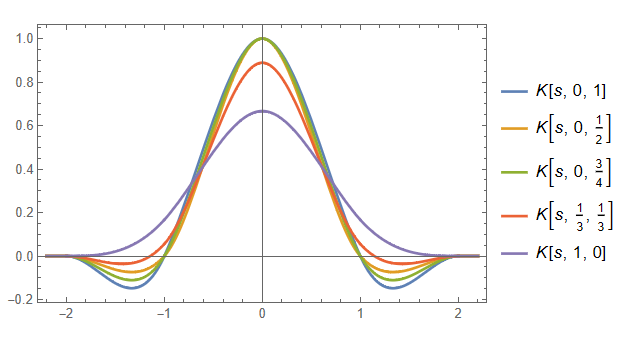
$B=0$인 경우는 $s=0$일 때 1이고, $|s|=1,2$일 0이므로 interpolation kernel($K(i-j)=\delta_{ij}$)에 해당한다. 그리고 $B=0, C=1/2$인 경우인 Catmul-Rom spline은 node에서 2차 도함수까지도 연속이므로 샘플링 데이터를 생성한 원 아날로그 함수에 $O(h^3)$이내에서 가장 유사하게 근사함을 보일 수도 있다.
// Mitchell Netravali Reconstruction Filter
// B = 0 C = 0 - Hermite B-Spline interpolator
// B = 0, C = 1/2 - Catmull-Rom spline
// B = 1/3, C = 1/3 - Mitchell Netravali spline
// B = 1, C = 0 - cubic B-spline
double MitchellNetravali(double x, double B, double C) {
x = fabs(x);
if (x >= 2) return 0;
double xx = x*x;
if (x >= 1) return ((-B - 6*C)*xx*x
+ (6*B + 30*C)*xx + (-12*B - 48*C)*x
+ (8*B + 24*C))/6;
if (x < 1) return ((12 - 9*B - 6*C)*xx*x +
(-18 + 12*B + 6*C) * xx + (6 - 2*B))/6;
}'Image Recognition > Fundamental' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Graph-based Segmentation (1) | 2024.05.26 |
|---|---|
| Linear Least Square Fitting: perpendicular offsets (0) | 2024.03.22 |
| Ellipse Fitting (0) | 2024.03.02 |
| Bilateral Filter (0) | 2024.02.18 |
| 파라미터 공간에서 본 최소자승 Fitting (0) | 2023.05.21 |




