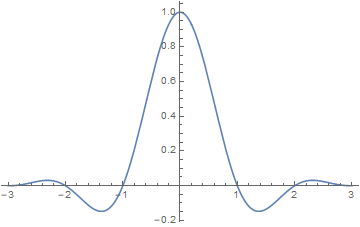
Lanczos kernel: a sinc function windowed by the central lobe of a second, longer, sinc function(wikipedia)
$$K(x) = \left\{ \begin {array}{ll} \text {sinc}(\pi x) \text {sinc}\Big( \frac {\pi x}{a}\Big), & |x| < a \\ 0 ,& |x| \ge a\end {array} \right. = \text{sinc}(\pi x) \text{sinc}\Big( \frac{\pi x}{a}\Big)\text{Box}(|x|<a) $$
$$H(\omega)=\frac{1}{2\pi^2\sqrt{2\pi}}\Big( -(2\pi-3\omega)\text{Si}(2\pi-3\omega)+(4\pi -3\omega)\text{Si}(4\pi-3\omega)$$$$+(2\pi +3\omega)\text{Si}(2\pi+3\omega)+(4\pi+3\omega)\text{Si}(4\pi+3\omega)\Big).$$
여기서 sine intergral은 다음과 같이 정의된다:
$$\text{Si}(x)=\int_0^x \frac{\sin(t)}{t} dt.$$

$x=0$ 근방에서는 Tayor 전개식을 이용하는 것이 더 효율적인다.

Lanczos kernel을 사용해서 일정한 간격으로 sampling 된 데이터 $\{f_i \}$를 보간하려고 할 때 보간함수 $F(x)$는 Lanczos kernel과 데이터의 convolution으로 표현할 수 있다.
$$ F(x) = \sum_{i \in \text{window}} f_i K(x - i) $$
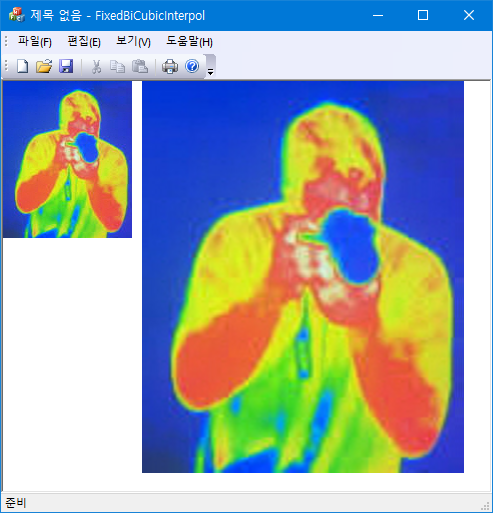
Interpolation 함수는 영상의 resampling 과정에서 사용할 수 있다. 주어진 이미지를 확대하거나 축소하려면 기존 이미지의 픽셀과 픽셀 사이 구간에서 픽셀 값을 알아내야 하는데, 이때 interpolation 함수를 이용하여 필요한 데이터를 얻는 과정인 resampling 한다.
다음 코드는 Lanczos3 kernel을 사용해서 이미지를 확대하거나 축소할 때 행에 대해서 필요한 resampling을 수행한다. 여기서는 kernel의 중심이 소스 이미지의 픽셀과 픽셀의 가운데에 놓이도록 설정하였다($-0.5$의 의미). 이는 작은 영상을 크게 확대할 때 가장자리에서 왜곡이 되는 것을 방지하기 위해서 인데 큰 영상을 확대/축소할 때는 영향이 없다. 이 interpolation은 separable이므로 2차원의 경우 행방향으로 진행한 후 그 결과를 다시 열 방향으로 진행하는 2-pass 방식으로 사용해도 된다.
// windowed sinc(x); window=sinc(x/3);
static double Lanczos3(double x){
if (x < 0) x = -x; // symmetric;
x *= PI;
if (x < 0.01) return 1. + (- 5./ 27. +
(14. / 1215. - 17. * x * x / 45927.) * x * x) * x * x;
else if (x < 3.) return 3. * sin(x) * sin(x / 3.) / x / x;
else return 0;
};
// interpolation in the horizonal direction: single channel or gray image;
// x = pixel position in a destination image;
double Lanczos3_line(BYTE *src_line, int srcWidth, int x, double xscale) {
double halfWidth;
if (xscale > 1.) halfWidth = 3.;
else halfWidth = 3. / xscale;
double centerx = double(x) / xscale - 0.5; //center loc of filter in the src_line;
int left = (int)floor(centerx - halfWidth);
int right = (int)ceil(centerx + halfWidth);
if (xscale > 1) xscale = 1;
double s = 0;
double weightSum = 0;
for (int ix = left; ix <= right; ix++) {
double weight = Lanczos3((centerx - ix) * xscale);
// for ix<0 || ix>=srcWidth: repeat boundary pixels
int xx = min(max(ix, 0), srcWidth - 1));
s += weight * src_line[xx];
weightSum += weight;
}
return s / weightSum;
}
이차원 이미지의 경우 수평방향의 적용한 후 다시 수직방향으로 적용하면 된다.
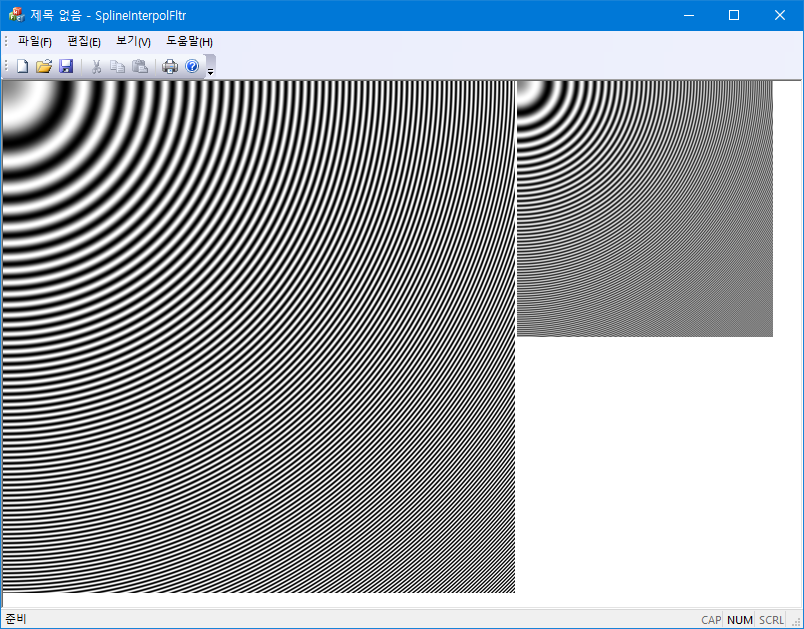

// 수평-수직을 동시함; 2 pass version으로 바꾸는 것이 더 효율적임;
void Lanczos3ResampleRGB(BYTE *src, int srcWidth, int srcHeight,
BYTE *dst, int dstWidth, int dstHeight)
{
const int bytes = 3; // = 1 for gray;
const double xscale = double(dstWidth) / srcWidth;
const double yscale = double(dstHeight) / srcHeight;
double halfWidth, scale;
if (yscale > 1.) {
halfWidth = 3; scale = 1;
}
else {
halfWidth = 3 / yscale; scale = yscale;
}
double color[3];
for (int y = 0; y < dstHeight; ++y) {
BYTE *pdst = &dst[y * dstWidth * bytes];
for (int x = 0; x < dstWidth; ++x) {
double csum[3] = {0}, weightSum = 0;
// dst geometry;
double centery = double(y) / yscale - 0.5;
int top = (int)floor(centery - halfWidth);
int bot = (int)ceil(centery + halfWidth);
for (int iy = top; iy <= bot; ++iy) {
double weight = Lanczos3((centery - iy) * scale);
int ys = max(0, min(iy, srcHeight - 1));
weightSum += weight;
Lanczos3_lineRGB(&src[ys * srcWidth * bytes], srcWidth, x, xscale, color);
for (int c = 0; c < bytes; ++c)
csum[c] += weight * color[c];
}
for (int c = 0; c < bytes; ++c) {
int a = int(csum[c] / weightSum);
*pdst++ = a < 0 ? 0: a > 255 ? 255: a;
}
}
}
}'Image Recognition > Fundamental' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Poisson Image Editing (0) | 2021.08.03 |
|---|---|
| Sampling Theorem (0) | 2021.05.12 |
| Interpolation Kernels (0) | 2021.05.05 |
| Fowler Angle (0) | 2021.04.05 |
| Brute-Force Euclidean Distance Transform (0) | 2021.03.14 |