RGB 컬러 이미지의 gray level의 cdf를 이용해서 histogram equalization을 수행한다. 컬러 이미지의 gray level은
$$gray = \frac{r + g+ b}{3}$$
으로 정의한다.
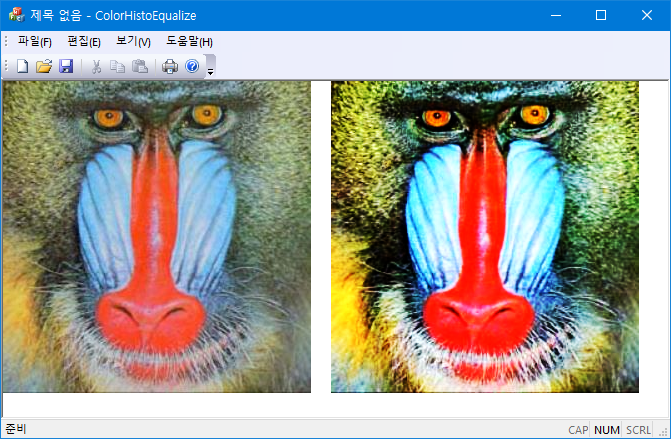
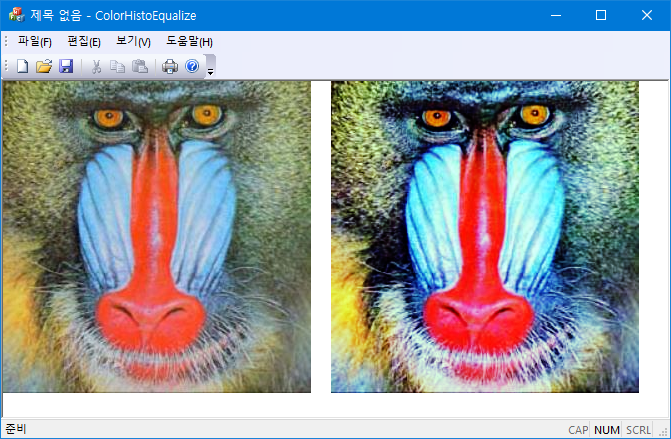
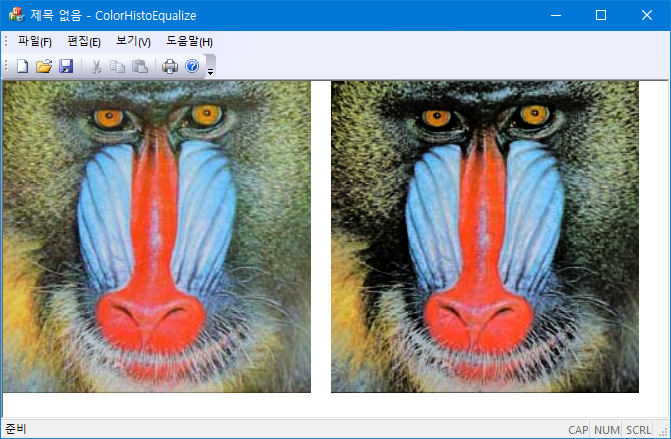
std::vector<BYTE> color_equalize_new(std::vector<BYTE> &rgb) {
int hist[256] = {0};
int chist[256], lut[256], partition[256 + 1];
std::vector<BYTE> out = raster; // clone;
// pdf of gray level: g = (r + g + b) / 3
for (int k = 0; k < rgb.size(); k += 3) {
int a = rgb[k+0]; a += rgb[k+1]; a += rgb[k+2];
++hist[a/3];
};
// cdf;
for (int i = 0, s = 0; i < 256; i++) {
s += hist[i]; chist[i] = s;
}
/* assign equal number of pixels in each gray levels;*/
int num_pixels = rgb.size()/3;
double pixels_per_level = double(num_pixels) / 256;
/* first and last in partition */
partition[0] = 0;
partition[256] = 256;
/* intermediate; */
for (int j = 0, i = 1; i < 256; i++) {
double desired = i * pixels_per_level;
while (chist[j + 1] <= desired) j++;
/* chist[j] <= desired < chist[j+1];*/
/* nearest interpolation */
if ((desired - chist[j]) < (chist[j+1] - desired)) partition[i] = j;
else partition[i] = j + 1;
}
/* Find i s.t. partion[i] <= j < partition[i+1];*/
for (int j = 0; j < 256; j++) {
int i = 0;
while (partition[i+1] <= j) i++;
lut[j] = i;
}
// needs hue preserving processes;
for (k = rgb.size(); k-->0;)
res[k] = lut[src[k]];
return out;
}std::vector<BYTE> color_equalize_HSV(std::vector<BYTE> &rgb) {
int hist[256] = {0};
int chist[256] = {0}, lut[256] = {0}, partition[256 + 1];
std::vector<BYTE> out = raster; // cloning;
std::vector<double> fH(rgb.size()/3);
std::vector<double> fV(rgb.size()/3);
std::vector<double> fS(rgb.size()/3);
const int n = rgb.size()/3;
double r, g, b;
for (int k = 0; k < rgb.size(); k += 3) {
b = rgb[k+0], g = rgb[k+1], r = rgb[k+2];
RGBtoHSV(r / 255, g / 255, b / 255, fH[k], fS[k], fV[k]);
};
// make histogram of V-color;
for (int k = n; k-->0;)
++hist[int(fV[k] * 255)];
// cdf;
for (int i = 0, s = 0; i < 256; i++) {
s += hist[i]; chist[i] = s;
}
/* assign equal number of pixels in each V-color;*/
int num_pixels = rgb.size()/3;
double pixels_per_level = double(num_pixels) / 256;
/* first and last in partition */
partition[0] = 0;
partition[256] = 256;
/* intermediate; */
for (int j = 0, i = 1; i < 256; i++) {
double desired = i * pixels_per_level;
while (chist[j + 1] <= desired) j++;
/* nearest interpolation */
if ((desired - chist[j]) < (chist[j + 1] - desired)) partition[i] = j;
else partition[i] = j + 1;
}
/* fill equalization LUT */
for (int j = 0; j < 256; j++) {
int i = 0;
while (partition[i + 1] <= j) i++;
lut[j] = i;
}
for (int k = n; k-->0;)
fV[k]= lut[int(fV[k] * 255)] / 255.;
for (int k = 0; k < rgb.size(); k += 3) {
HSVtoRGB(fH[k], fS[k], fV[k], r, g, b);
out[k+0] = int(b * 255);
out[k+1] = int(g * 255);
out[k+2] = int(r * 255);
}
return out;
}/* fR Red component, range: [0, 1]
** fG Green component, range: [0, 1]
** fB Blue component, range: [0, 1]
** fH Hue component, range: [0, 360]
** fS Hue component, range: [0, 1]
** fV Hue component, range: [0, 1] */
void RGBtoHSV(double fR, double fG, double fB, double& fH, double& fS, double& fV);
void HSVtoRGB(double fH, double fS, double fV, double& fR, double& fG, double& fB);728x90
'Image Recognition > Fundamental' 카테고리의 다른 글
| FFT를 이용한 영상의 미분 (0) | 2022.02.12 |
|---|---|
| SVD Fitting (0) | 2022.02.07 |
| Least Squares Fitting of Ellipses (0) | 2022.01.27 |
| Circle Fitting: Pratt (0) | 2022.01.20 |
| Best-fit Ellipse 2 (0) | 2022.01.18 |




