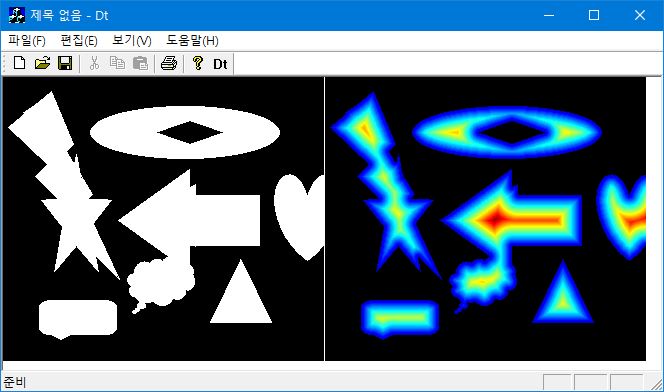
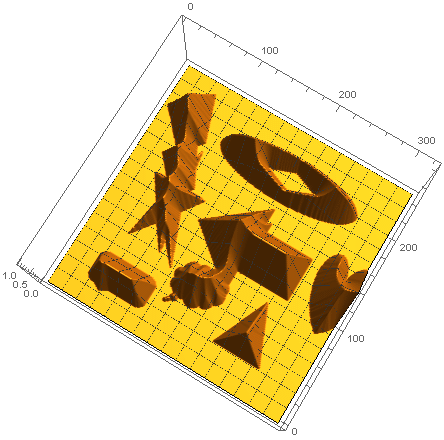
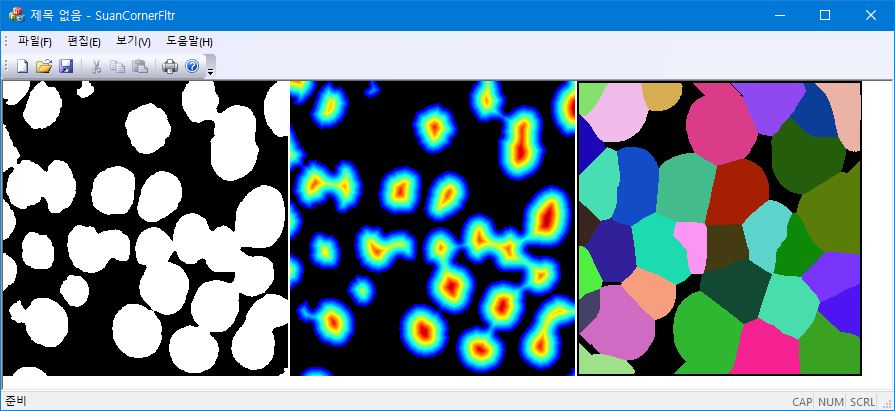
배경의 각 픽셀에 인접 픽셀까지의 수평/수직 방향으로는 Euclidean distance가 1 만큼 떨어져 있고, 대각선 방향으로는 $\sqrt{2}$만큼 떨어져 있다. 이 거리에 $\sqrt{8}\approx 2.83\approx 3$을 곱하면 거리를 각각 $3$과 $4$로 근사할 수 있어서 정수 연산 만으로 distance transform을 구할 수 있다.



#define BACKGROUND (0)
void distanceTransform_approx(BYTE **image, int w, int h, int **map) {
// initialization;
for (int y = h; y-->0;)
for (int x = w; x-->0;) map[y][x] = 0;
// forward_pass
// y=x=0;
if (image[0][0] == BACKGROUND) map[0][0] = 0xFFFF;// INFINITY;
// y=0;
for (int x=1; x<w; x++)
if (image[0][x] == BACKGROUND) map[0][x] = 3 + map[0][x-1];
for (int y=1; y<h; y++) {
// x=0;
if (image[y][0] == BACKGROUND)
map[y][0] = min(3 + map[y-1][0], 4 + map[y-1][1]);
for (int x=1; x<w-1; x++)
if (image[y][x] == BACKGROUND)
map[y][x] = min(4 + map[y-1][x-1], min(3 + map[y-1][x],
min(4 + map[y-1][x+1], 3 + map[y][x-1])));
// x=w-1;
if (image[y][w-1] == BACKGROUND)
map[y][w-1] = min(4 + map[y-1][w-2], min(3 + map[y-1][w-1], 3 + map[y][w-2]));
}
// backward_pass
// y=h-1;
for (int x = w-1; x-->0;)
if (image[h-1][x] == BACKGROUND)
map[h-1][x] = min(map[h-1][x], 3 + map[h-1][x+1]);
for (int y = h-1; y-->0;) {
// x=w-1;
if (image[y][w-1] == BACKGROUND)
map[y][w-1] = min(map[y][w-1], min(3 + map[y+1][w-1], 4 + map[y+1][w-2]));
for (int x=w-1; x-->1;)
if (image[y][x] == BACKGROUND)
map[y][x] = min(map[y][x], min(4 + map[y+1][x+1],
min(3 + map[y+1][x], min(4 + map[y+1][x-1], 3 + map[y][x+1]))));
// x=0;
if (image[y][0] == BACKGROUND)
map[y][0] = min(map[y][0], min(4 + map[y+1][1],
min(3 + map[y+1][0], 3 + map[y][1])));
}
};728x90
'Image Recognition > Fundamental' 카테고리의 다른 글
| FFT 구현 (0) | 2024.07.31 |
|---|---|
| CLAHE (2) (1) | 2024.06.26 |
| Graph-based Segmentation (1) | 2024.05.26 |
| Linear Least Square Fitting: perpendicular offsets (0) | 2024.03.22 |
| Cubic Spline Kernel (1) | 2024.03.12 |