지문에서 ridge의 방향(orientation)은 gradient에 수직한 방향이다(그런데 벡터인 gradient와는 달리 ridge의 방향은 모호함이 있다. 시계방향 또는 반시계방향으로 90도 회전이 모두 동일한 ridge의 방향이다). gradient의 방향각이 $\alpha$일 때 수직인 ridge의 방향각은 $\theta =\frac{\pi}{2} + \alpha$로 정의하자. 방향각을 주어진 gradient 성분 $\nabla I = (g_x, g_y)$로 표현하기 위해서
$$ \sin 2\alpha = 2 \sin \alpha \cos \alpha = 2 \frac{g_x}{\sqrt{g_x^2 + g_y^2}}\frac{g_y}{\sqrt{g_x^2 + g_y^2}}$$
$$\cos 2\alpha = \cos^2 \alpha - \sin^2\alpha = \frac{g_x^2}{g_x^2 + g_y^2} -\frac{g_y^2}{g_x^2 +g_y^2}$$
임을 이용하자. $$\tan 2\alpha = \frac{ 2g_x g_y}{ g_x^2 - g_y^2}$$로 쓸 수 있으므로 ridge의 방향각은
$$ \theta =\frac{\pi}{2} + \frac{1}{2} \arctan \frac{2g_x g_y}{g_x^2 - g_y^2}$$
임을 알 수 있다. $(g_x, g_y) \rightarrow (-g_x, -g_y)$이더라도 ridge의 방향은 동일하므로 $\theta$의 범위는 $0\le \theta < \pi$로 제한된다.
이미지의 한 지점에서 ridge의 방향은 그 점을 중심으로 하는 적당한 크기의 윈도 평균값으로 추정한다. gradient 성분은 Sobel 연산자나 Prewitt 연산자를 convolution해서 얻을 수 있다. 따라서 지문 이미지 상의 픽셀 좌표 $(i,j)$에서 ridge의 방향은
$$\theta_{ij} = \frac{\pi}{2} +\frac{1}{2}\arctan \frac{2 G_{xy}}{G_{xx} - G_{yy}}$$
$$ G_{xy} = \sum_{W} \text{gradX}_{ij} \times \text{gradY}_{ij}$$
$$ G_{xx} = \sum_{W} \text{gradX}_{ij} \times \text{gradX}_{ij}$$
$$ G_{yy} = \sum_{W} \text{gradY}_{ij} \times \text{gradY}_{ij}$$
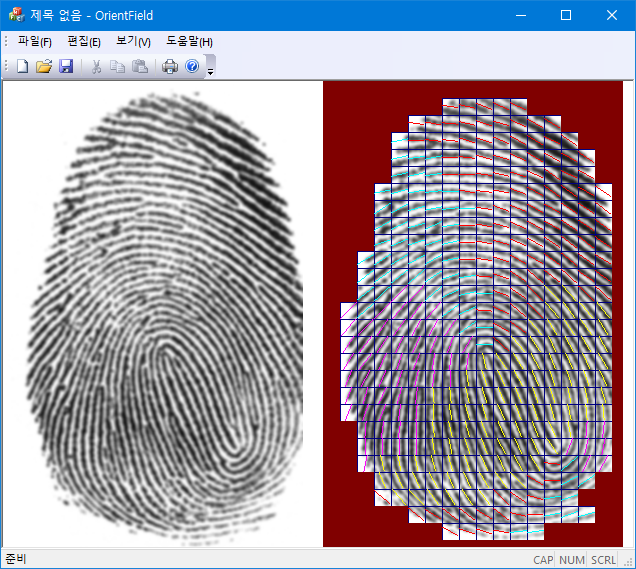
아래 결과는 5x5 크기의 Gaussian filter를 적용한 지문 이미지에 17x17 크기의 윈도를 겹치지 않게 잡아서 평균을 계산한 결과다. $G_{xx}+G_{yy}$가 최대값의 $20\%$보다 작은 영역은 방향을 표시하지 않았다 (red:0~45, yellow:45~90, magenta: 90~135, cyan: 135~180).
int RidgeOrientaion(BYTE *img, int w, int h, int bsz/*17*/, double *omap) {
const int nn[] = {-w - 1, -w, -w + 1, -1, 0, 1, w - 1, w, w + 1};
const int sobelX[] = {-1, 0, 1, -2, 0, 2, -1, 0, 1};
const int sobelY[] = {-1, -2, -1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 2, 1};
const int xmax = w - 1, ymax = h - 1;
std::vector<int> gradx(w * h, 0);
std::vector<int> grady(w * h, 0);
for (int y = 1, pos = w; y < ymax; y++) {
pos++; //x = 0;
for (int x = 1; x < xmax; x++, pos++) {
int sx = 0, sy = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < 9; k++) {
int v = img[pos + nn[k]];
sx += sobelX[k] * v;
sy += sobelY[k] * v;
}
gradx[pos] = sx;
grady[pos] = sy;
}
pos++; // x = xmax;
}
const int ny = h / bsz;
const int nx = w / bsz;
for (int iy = 0; iy < ny; iy++) {
for (int ix = 0; ix < nx; ix++) {
int sxy = 0, sxx = 0, syy = 0;
int pos = (iy * w + ix) * bsz; //starting position of block(ix, iy)
int *dx = &gradx[pos];
int *dy = &grady[pos];
for (int jj = 0; jj < bsz; jj++) {
for (int ii = 0; ii < bsz; ii++) {
int gx = dx[jj * w + ii];
int gy = dy[jj * w + ii];
sxy += gx * gy;
sxx += gx * gx;
syy += gy * gy;
}
}
omap[iy * nx + ix] = 0.5 * (PI + atan2(double(2.0 * sxy), double(sxx - syy)));
}
}
//...identify fingerprint regions and draw orientation map;
return 1;
}'Image Recognition' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Edge Preserving Smoothing (0) | 2024.02.14 |
|---|---|
| Watershed Segmentation (0) | 2021.02.27 |
| Contrast Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization (CLAHE) (3) | 2021.02.15 |
| Fixed-Point Bicubic Interpolation (1) | 2021.01.19 |
| Distance Transform (0) | 2021.01.16 |