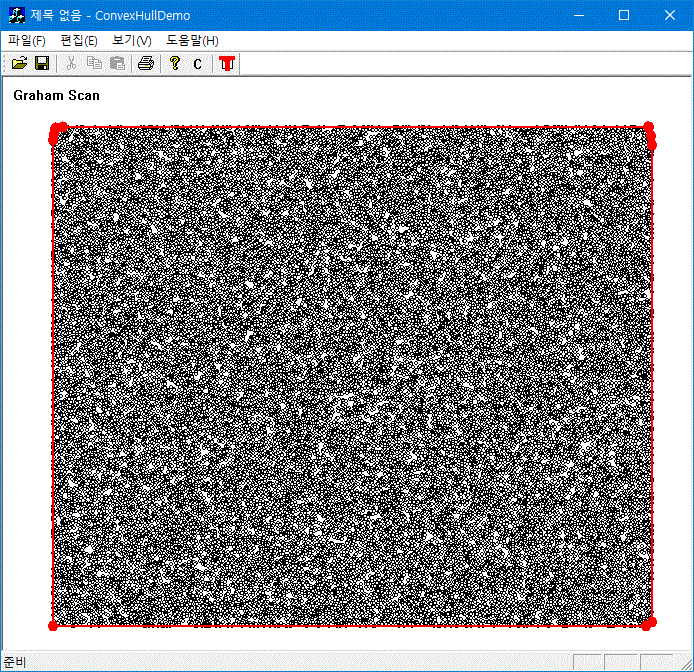
Convex hull을 찾을 때, 중복점과 일직선상 위에 있는 점들에 대해서 적절한 처리를 하지 않으면 효율적으로 작성된 알고리즘이라도 정상적으로 동작하지 않을 수 있다. 그림은 Graham Scan 알고리즘을 이용해서 50,000개 점들의 convex hull을 구한 결과다. 각 정렬을 하기 위해서는 pivort point가 필요한데 std::sort()을 호출할 때 compare()에서 global 변수를 쓰지 않기 위해서 첫 원소를 pivot point로 잡아서 사용한다. 정렬 후에는 빼주었던 pivot를 다시 더해준다.
inline int LeftSide(const CPoint &A, const CPoint &B, const CPoint &C) {
return (B.x - A.x) * (C.y - A.y) - (C.x - A.x) * (B.y - A.y); // cross(AB, AC);
}
static int cross(const CPoint &p1, const CPoint &p2) {
return p1.x * p2.y - p1.y * p2.x;
}
static int norm2(const CPoint &p) {
return p.x * p.x + p.y * p.y;
}
static int compare(const CPoint &a, const CPoint &b) {
int ccw = cross(b, a);
// 거리가 먼 곳 --> 가까운 곳;
if (ccw == 0) return norm2(b) < norm2(a);
return ccw < 0; // 반시계방향 정렬;
}
static void angularSort(std::vector<CPoint> & pts) {
if ((pts.size()) < 2) return;
int id = 0;
for (int i = pts.size(); i-->0;)
if ((pts[id].y > pts[i].y) || (pts[id].y == pts[i].y && pts[i].x > pts[id].x))
id = i; //lowest--y-value; //largest--x-value;
std::swap(pts[0], pts[id]);
for (int i = pts.size(); i-->1;) pts[i] -= pts[0];
std::sort(pts.begin()+1, pts.end(), compare);
for (int i = pts.size(); i-->1;) pts[i] += pts[0];
};
// AB와 BC가 나란할 때, AB 방향과 BC방향이 같은가(0) 반대면 (1): dot(AB, BC);
static int folded(const CPoint &A, const CPoint &B, const CPoint &C) {
return (B.x - A.x) * (C.x - B.x) + (B.y - A.y) * (C.y - B.y) <= 0;
}
std::vector<CPoint> GrahamScan(const std::vector<CPoint>& points) {
if (points.size() < 3) return std::vector<CPoint> (); //null_vector;
std::vector<CPoint> pts = points; //clone;
angularSort(pts);
std::vector<CPoint> hull(pts.size());
hull[0] = pts[0];
int i = 1;
while (i < pts.size()) {
// peek out points degenerate with pts[0];
if (pts[i] != hull[0]) {
hull[1] = pts[i++]; break; // (i++)
}
i++;
}
if (i == pts.size()) return std::vector<CPoint> ();//null_vector;
int k = 2; // 새로 추가되는 hull index;
while (i < pts.size()) {
// (i)가 hull의 left에 있으면(1) hull의 꼭지점에 추가;
int ccw = LeftSide(hull[k - 2], hull[k - 1], pts[i]);
if (ccw > 0) hull[k++] = pts[i++];
// (i)가 hull의 직전 변과 collinear한 데 반대방향을 향하면 skip;
else if (ccw == 0 && folded(hull[k - 2], hull[k - 1], pts[i])) ++i;
// (i)가 hull의 right 또는 위에 있으면(직전 변과 같은 방향)
// hull의 직전 꼭지점을 순차적으로 제거한 후 다시 검사;
else --k;
ASSERT(k >= 2);
}
hull.resize(k);
return hull;
};728x90
'Computational Geometry' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Rotating Calipers (3) | 2021.03.31 |
|---|---|
| Convex Hull Peeling (0) | 2021.03.29 |
| Jarvis March (0) | 2021.03.26 |
| Approximate Minimum Enclosing Circle (1) | 2021.03.18 |
| Minimum Bounding Rectangle (3) | 2021.03.15 |




