$$I = \int_0^\infty \frac{x^adx}{(1+x)^2 } = \frac{\pi a}{\sin \pi a } ~~~~(-1 < a<1) $$
복소함수
$$ f(z) = \frac{z^a}{(1+z)^2}$$
을 그림의 contour를 따라 적분한다. $f(z)$는 $z=0,\infty$이 branch point 이므로 cut line을 $+x$ 축으로$(0\le\arg(z)\le2\pi$) 잡았다. $z=-1$은 double pole이다.
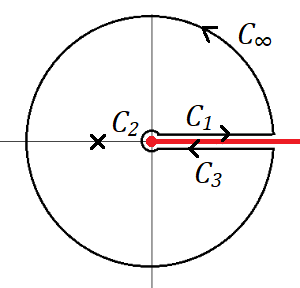
경로 $C_1$에서 $ z= x e^{i 0} ~~(x: 0 \to \infty)$이므로
$$\int_{C_1} f(z)dz = \int_0^\infty \frac{x^a }{(1+x)^2 }dx = I$$
경로 $C_3$에서 $ z= x e ^{i 2\pi} ~~(x: \infty \to 0)$이므로
$$ \int_{C_3} f(z) dz = \int_\infty^0 \frac{x^a e^{i 2\pi a} }{(1+x)^2 }dx = - e^{i 2\pi a }I $$
경로 $C_2$에서 $z=\epsilon e^{i \theta}~(\theta:0\to 2\pi)$이므로
$$\int_{C_2} f(z)dz = O( \epsilon^{1+a} ) \rightarrow 0.$$
경로 $C_\infty$에서 $z= R e^{ i \theta}$로 쓰면
$$\int_{C_\infty} f(z) dz = O(R^{a-1}) \rightarrow 0.$$
그리고, $z=-1=e^{i\pi}$에서 residue값은
$$\text{Res}f(z=e^{i\pi} ) =\frac{dz^a}{dz} (z=e^{i\pi}) = a(e^{i\pi})^{a-1}=-a e^{i\pi a}$$ 따라서 residue 정리에 의해
$$\sum \int_{C_k} f(z) dz = 2\pi i \times \text{Res}f(e^{i \pi}) $$
$$ (1- e^{i2\pi a} ) I = 2\pi i (-a e^{i\pi a}) ~~~~\to ~I= \frac{\pi a}{\sin \pi a}$$

'Mathematics' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 주어진 길이의 폐곡선으로 가둘 수 있는 최대 면적의 도형은? (0) | 2020.02.15 |
|---|---|
| Integration along a branch cut-005 (0) | 2017.07.02 |
| Integration along a branch cut-004 (0) | 2017.06.29 |
| Integration along a branch cut-003 (0) | 2017.06.28 |
| Integration along a branch cut-001 (0) | 2017.06.27 |




